
COVID-19 Update for Virginia
December 29, 2021
Dear Colleague:
Thank you for your continued partnership in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic. Please visit the Virginia Department of Health (VDH) website for current clinical and public health guidance, epidemiologic data, and other information. Updates on the following topics are included in this correspondence:
- Updated and Shortened Isolation and Quarantine Guidance for the General Population
- Updated Guidance for the Management of Healthcare Personnel with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Exposure
- Therapeutics Update
Updated and Shortened Isolation and Quarantine Guidance for the General Population
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) updated isolation and quarantine guidance for the general population. People with COVID-19 may end isolation after 5 days if asymptomatic or if their symptoms are resolving. They should continue to wear a mask when around others for an additional 5 days. These recommendations apply regardless of vaccination status. The isolation period was shortened from 10 days because current evidence shows that most SARS-CoV-2 transmission occurs closer to the onset of illness, generally in the 1–2 days before and the 2–3 days after symptoms begin.
CDC also changed and shortened quarantine guidance for those exposed to COVID-19:
- People who have been boosted or completed the Johnson & Johnson (J&J) primary series within the last 2 months or completed an mRNA primary series within the last 6 months are not required to quarantine following an exposure to someone with COVID-19. When around others, they should wear a mask for 10 days after exposure.
- People who are unvaccinated or completed the J&J primary series more than 2 months ago and are not boosted or completed an mRNA primary series more than 6 months ago and are not boosted should quarantine for 5 days following exposure to someone with COVID-19 and continue to wear a mask for an additional 5 days. If an individual cannot feasibly quarantine, they must wear a mask for 10 days after exposure.
Regardless of vaccination status, those exposed to someone with COVID-19 should get tested on day 5, if possible. They should also isolate immediately if they develop symptoms or test positive.
At this time, CDC recommends following September 2021 isolation and quarantine guidance for healthcare patients and nursing home residents. We anticipate that CDC will update sector specific guidance shortly.
CDC’s updated quarantine guidance reflects data from South Africa and the United Kingdom, which show that vaccine effectiveness against Omicron infection after two doses of mRNA vaccine is about 35%. Following a booster dose, vaccine effectiveness against Omicron infection increases to 75%. Please continue to encourage all patients 16 years and older to get their COVID-19 booster shots when they are eligible and everyone 5 years and older to complete their primary series.
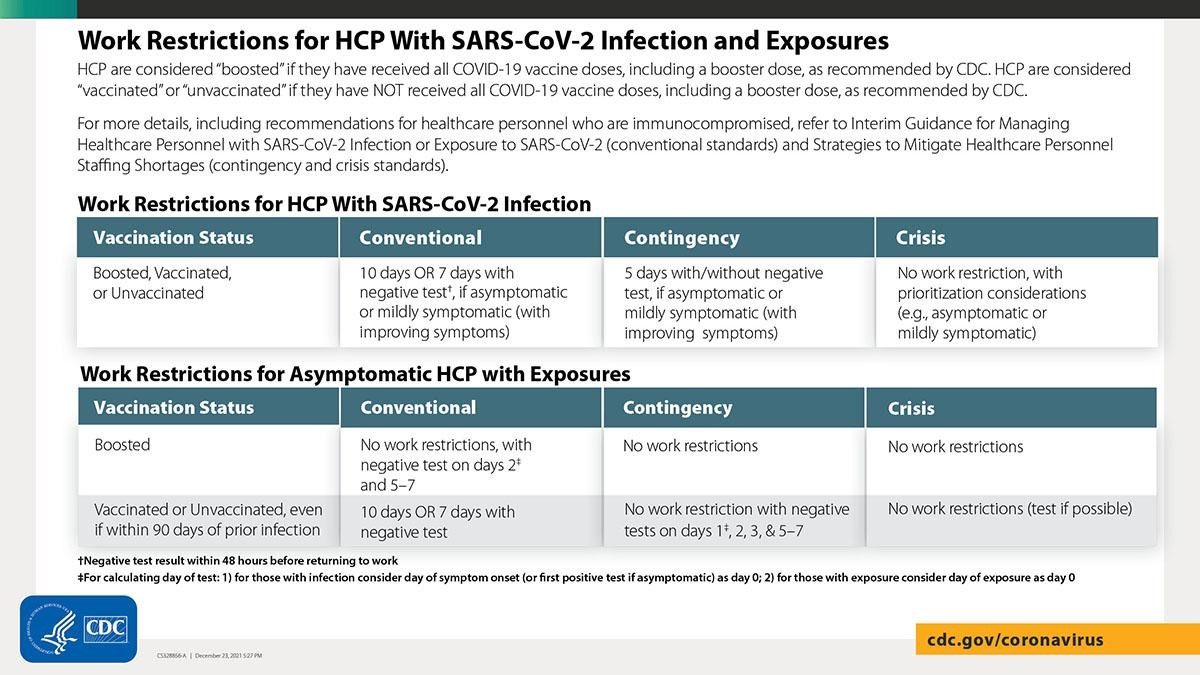
Updated Guidance for the Management of Healthcare Personnel with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Exposure
CDC released updated guidance for isolation and quarantine for healthcare personnel (HCP), decreasing their isolation time after infection with COVID-19. Additionally, CDC released updated guidance for contingency and crisis management in the setting of significant healthcare worker shortages. The new general population isolation and quarantine guidance detailed above does not apply to HCP; healthcare facilities should implement the following guidance for HCP:
- Interim Guidance for Managing Healthcare Personnel with SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Exposure to SARS-CoV-2
- Strategies to Mitigate Healthcare Personnel Staffing Shortages
- Health Alert Network (HAN) Health Advisory
Healthcare facilities including nursing homes may implement new CDC guidance for contingency and crisis conditions to shorten duration of work restrictions for HCP when needed to alleviate healthcare staffing shortages. The guidance is based on the limited information currently available about the Omicron variant and will be updated as needed as new information becomes available. HCP with even mild symptoms of COVID-19 should be prioritized for viral testing. Ensure that SARS-CoV-2 testing is performed with a test that can detect SARS-CoV-2 considering currently circulating variants.
Return to work for HCP with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Under conventional conditions, HCP with SARS-CoV-2 infection who are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic with improving symptoms can return to work after 7 days with a negative test, and the isolation time period can be further shortened if there are staffing shortages (see table below).
Return to work for asymptomatic HCP with exposure:
- Asymptomatic HCP who have received all recommended COVID-19 vaccine doses, including a booster, do not need to quarantine at home following higher-risk exposures (see table below for testing guidance under conventional conditions for higher-risk exposures).
- Asymptomatic HCP who have not received all COVID-19 vaccine doses, including a booster dose, can return to work prior to the previously recommended 14-day quarantine period, assuming they do not develop symptoms or test positive for SARS-CoV-2 (see table below for testing guidance for higher-risk exposures).
- Asymptomatic HCP with a lower-risk exposure, whether boosted, vaccinated, or unvaccinated, do not have work restrictions or testing recommendations.
- Refer to the CDC table for Recommended Work Restrictions for HCP Based on Vaccination Status and Type of Exposure for more information on types of exposures.
Therapeutics Update
Last week, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized the first oral antivirals for the treatment of COVID-19.
- Pfizer’s Paxlovid, a combination of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, is authorized to treat mild to moderate documented COVID-19 in adults and pediatric outpatients (12 years of age and older weighing at least 40 kg [88 pounds]) who are at high-risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
- Merck’s molnupiravir is authorized for the treatment of mild to moderate documented COVID-19 in adults who are at high-risk for progression to severe COVID-19 and for whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options authorized by the FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate.
Both treatments are available by prescription only and should be initiated as soon as possible after diagnosis of COVID-19 and within 5 days of symptom onset. Paxlovid and molnupiravir will be available in some pharmacies in the Commonwealth starting this week; however, initial supplies of both medications will be very limited. As pharmacies receive these antivirals, a list of locations in Virginia will be available on the Therapeutics webpage.
EVUSHELD (tixagevimab with cilgavimab, AstraZeneca) is FDA authorized for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against COVID-19 in patients aged 12 years and older who are moderately to severely immunocompromised, or for whom COVID-19 vaccine is not medically recommended due to a history of a severe adverse reaction to a COVID-19 vaccine or one of its components. Virginia has a limited supply of EVUSHELD available for distribution; the initial supply will go to existing monoclonal antibody administration sites.
The Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) plans to pause shipments to states of bamlanivimab and etesevimab together, etesevimab alone, and REGEN-COV effective January 3, 2022, pending updated CDC data, because current data show it’s unlikely that bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together (Bam/Ete) or casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) will be effective against the Omicron variant. Sotrovimab appears to retain activity against the Omicron variant. FDA updated the Health Care Provider Fact Sheets for bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together, REGEN-COV, and sotrovimab with specific information regarding expected activity against the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529/BA.1).
Thank you again for your continued partnership as we respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. I hope you have a safe and happy holiday season.
Sincerely,
M. Norman Oliver, MD, MA
State Health Commissioner

